Virtual Reality Explained
You’ve likely heard the term “virtual reality” thrown around in recent years, especially in relation to massive tech conglomerates like Meta or Unity. But what applications does VR have beyond entertainment?
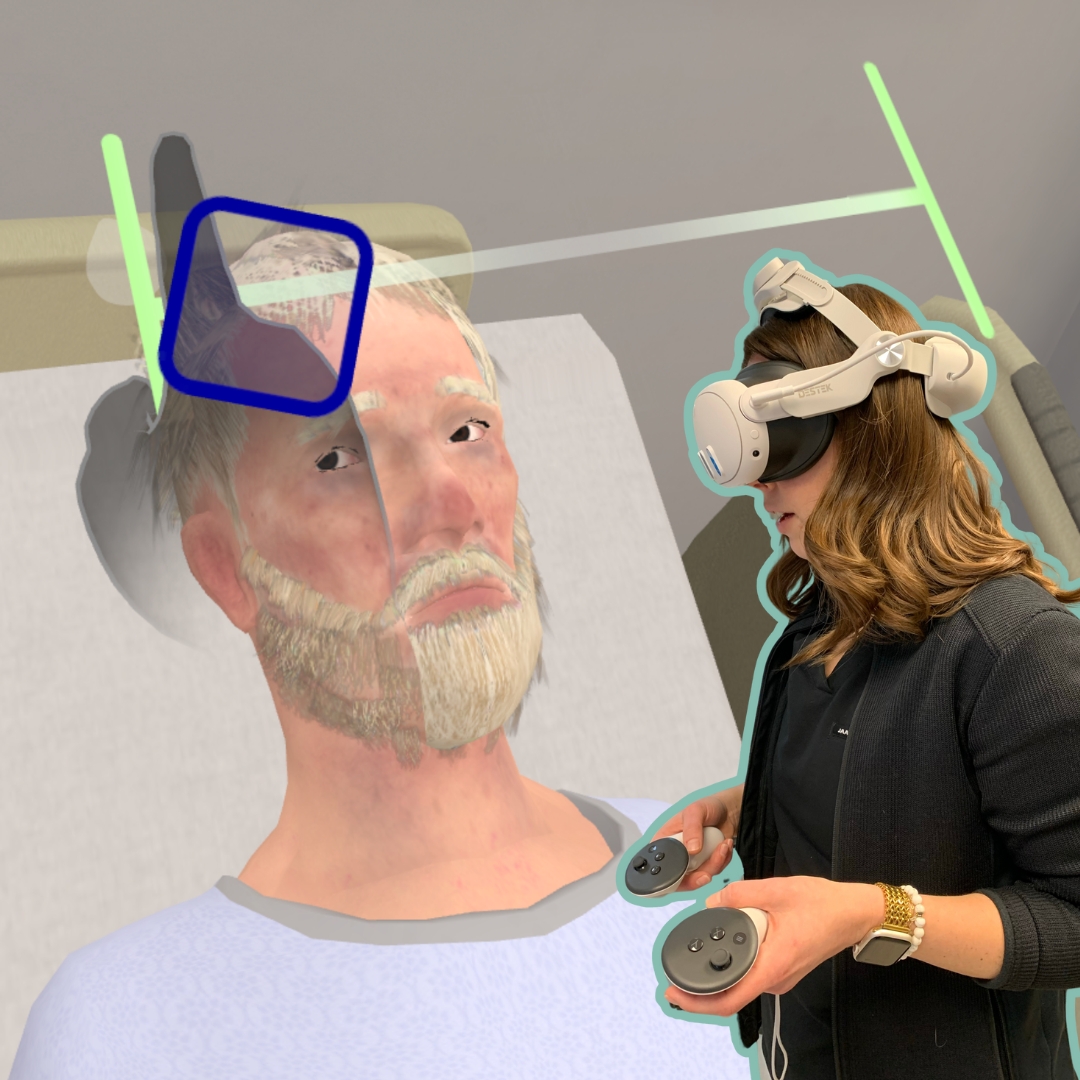
Virtual Reality, or “VR,” uses computer technology to create a simulated, three-dimensional environment for exploration and instruction. Unlike traditional two-dimensional or flat computer interfaces, VR places the user inside the virtual environment which creates a fully immersive experience.
This immersive experience serves as an optimal training tool because it contains situations that mimic real life and allows users to conveniently practice on their own time and terms. Nowhere is the potential for VR training greater and more essential than in clinical healthcare settings.
Dr. Nick West, Chief Medical Officer and Divisional Vice President of Global Medical Affairs at Abbott’s Vascular Division explains, “Just as pilots learn on flight simulators before taking to the skies… VR training programs allow physicians to interact, learn, and train before translating these skills to real-world procedures.”
The acceleration of digital learning has shown that a combination of virtual reality-based training and traditional, in-person training can set clinical teams up for success as they navigate an increasingly fraught healthcare environment.
Let’s explore some of the common misconceptions and established benefits of VR training for healthcare.
Common Misconceptions About VR
VR is a relatively new technology (at least in its current applications), and the standard consumer may have many common misunderstandings about its uses and reliability.
Here are some of the general misconceptions we hear about virtual reality.
“I’m probably going to get motion sickness or dizzy from wearing a headset.”
VR technology has come a very long way since its inception and continues to make improvements in user experience. The Health Scholars team has found that few people report feeling sick in our VR scenarios. We develop applications with this sensitivity in mind and take great care in the design process(72 frames per second, to prevent dizziness), as few of our users have significant VR gaming experience. Our apps can also be completed from a seated position, which can prevent or improve symptoms if users do experience any potential side effects.
“I can’t afford VR headsets and training. It’s going to be pretty expensive, right? Plus, I’ll have to purchase new computers or other hardware.”
Health Scholars’ VR headsets are readily available for as little as $300 and act as computers in their own right; they only require wireless internet to fully function. They contain all the hardware needed to run our applications, and with only a wireless headset, the user can run through our training simulations at any time, in any place.
“My team isn’t very tech-savvy. How are they going to be able to use VR in a professional clinical setting?”
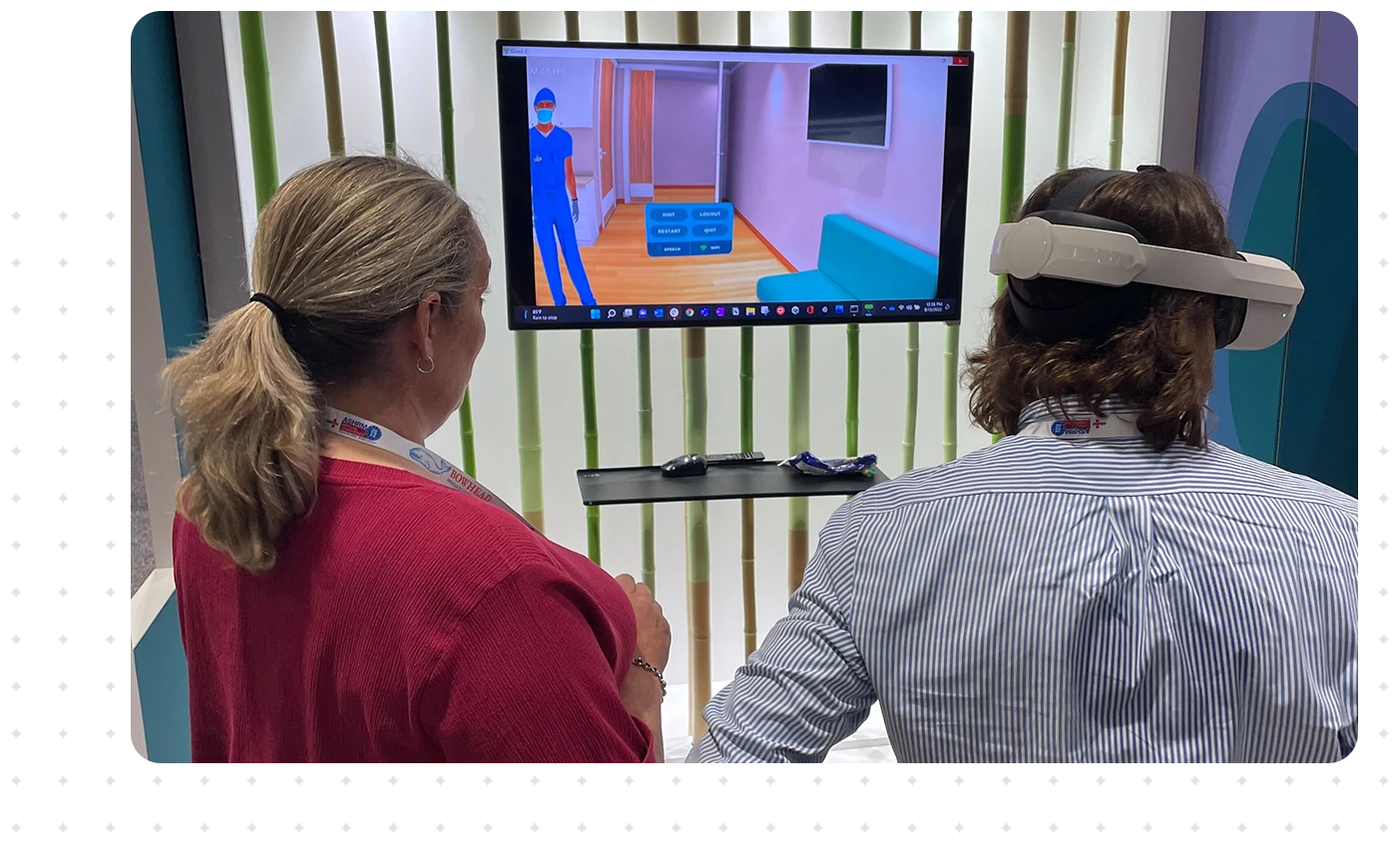
Our team is committed to getting your staff squared away from day one. Each individual headset comes complete with VR onboarding, and we provide detailed training on how to use the applications. The Health Scholars Help Center also provides helpful post-implementation tips and tricks.
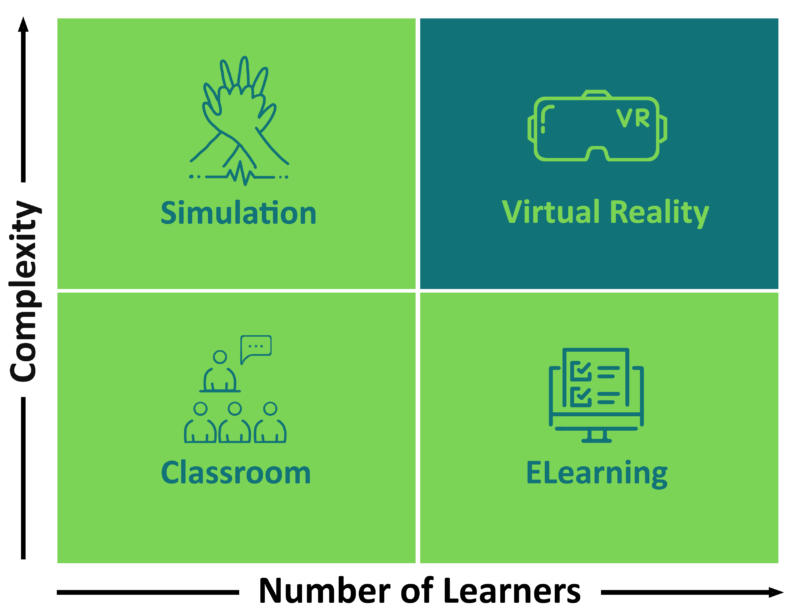
Three Advantages of VR Training for Clinicians
E-learning, classroom training, and high-fidelity simulations all play a part in the holistic curriculum for a learner. Virtual reality is the sweet spot, the combination of all of the best parts of these learning modalities. It drives users to pursue interactive learning — scientifically proven to be more effective over time.
VR training in a clinical setting has numerous tangible benefits, but we’ve identified three of the most relevant and effective.
Low Cost
Simulation-based training is a costly expense for any hospital – a single human patient simulator or manikin can cost anywhere from $10,000 to $100,000 depending on the type, brand, features, and included support services, while simulation centers also carry a significant cost and time expense.
On the other end of the learning spectrum, classroom training and e-learning modules are both productive and cost-effective solutions, but they don’t have the same interactive elements that simulation-based training has.
VR mimics high-fidelity learning and can be done repeatedly, as many times as a user wants, without incurring exponential costs. These learners can go at their own pace, and at a low-cost point, you reinforce their learning while decreasing any harmful knowledge decay.
Safe Environment
VR training provides a safe, comfortable environment in which clinicians practice, learn, facilitate, and take on leadership roles. Users are immersed in a variety of realistic healthcare settings and practice care in a way that feels realistic and urgent, helping them stay focused on the patient’s safety.
It also creates a space for users to feel confident even if they make mistakes. Because individuals practice on their own time and with virtual teammates, they don’t have to experience shame or fear in their decisions.
Scalable Growth
Since VR headsets aren’t individually tied to single users, it’s possible to scale up the number of users per headset.
From a logistics perspective, it usually takes one person around 20+ minutes to go through a single training module. That ends up being around two trainees per hour, which works out to about 16-20 trainees per day. If you have more than one VR headset in your organization, this multiplies exponentially.
HealthScholars and VR Training for Clinicians
Health Scholars is the only company currently using AI voice-guided technology in VR simulations. Our proprietary voice technology produces a truly interactive experience – clinicians use their voice to instruct, command, and communicate with both real-life and virtual users.
Our apps have configurability to accommodate any of your protocols, and they’re developed with practicing clinicians, evidence-based guidelines, national specialty organizations, and clinical educators to address real-world patient safety problems.
We support three primary clinical areas with specific applications for each:
- Perioperative Care – Malignant Hyperthermia, Fire Safety, and more
- Emergency Care – ACLS, Stroke Assessment, and more
- Labor & Delivery – Obstetric Emergencies, Fetal Heart Monitoring, and more
Users in the headsets can practice alone as the leader of a team of providers in a realistic healthcare environment, and they can feel free to “try their first instincts” without the stress of embarrassment in front of their teammates or supervisors.
Plus, our Performance Dashboard gives you tangible and actionable insights through user scoring, user and readiness reports, and debriefs, while our superior customer service team facilitates utilization so you can maximize the value of each seat.
Learn More
Ready to schedule a demo or simply chat with a member of our team? Reach out to us and let’s start a conversation.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
- Cosmos 2.0: The Future of VR Training is Here March 4, 2025
- Introducing Cosmos 1.0! July 15, 2024
- Introducing the Meta Quest 3 November 21, 2023
- Revolutionizing Medical Training with Custom VR Content November 8, 2023
- Pediatric Emergency Care in Home (PEC) November 2, 2023